July 22, 2021
Biden’s VA Budget Gets Strong Support in House Appropriations Action


Last month, FBIQ reported on the Biden Administration’s $270 billion FY22 Budget for the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). The House Appropriations Committee (HAC) held subcommittee and full committee markups of the FY22 Military Construction and Veterans Affairs bill on June 24 and June 30. The legislation, H.R. 4355, was reported out of Committee on a partisan 33-24 vote and now awaits consideration by the full House. The Senate has not marked up any spending bills nor announced a schedule to do so.
While there is bipartisan support for VA funding, HAC Republicans voted against the FY22 spending bill, citing concerns regarding overall funding levels and policy issues. As Ranking Member Granger (R-TX) stated on June 30, “Unfortunately, this bill is based on a funding framework that the Majority Party developed without Republican support. This difference of opinion on both funding priorities and policy positions could slow down our appropriations process this year.” For the first time in a decade, funding totals for FY22 are not bound by law. House Democrats are marking to a $1.5 trillion total aligned with Biden’s FY22 Budget. Republicans argue that total is too high and Democrats are underfunding national defense.
This legislation meets our solemn, Constitutional responsibility to provide for our nation’s veterans…As our military and Department of Veterans Affairs continue to overcome unprecedented challenges associated with COVID-19, we have a responsibility to make certain that they are supported.
House Appropriations Committee Chairwoman DeLauro (D-CT), June 29
The HAC-approved bill fully funds Biden’s FY22 VA Budget, and focuses on veterans’ services and needs, including telehealth access, suicide prevention, opioid treatment, homelessness, cybersecurity, and use of informatics and personalized medicine. The Committee bill provides $113.1 billion in discretionary funding, an $8.5 billion increase over the FY21 level and $25 million more than Biden’s Budget (Chart I). These totals do not include Medical Collections, which are estimated to be between $3-4 billion in FY22.
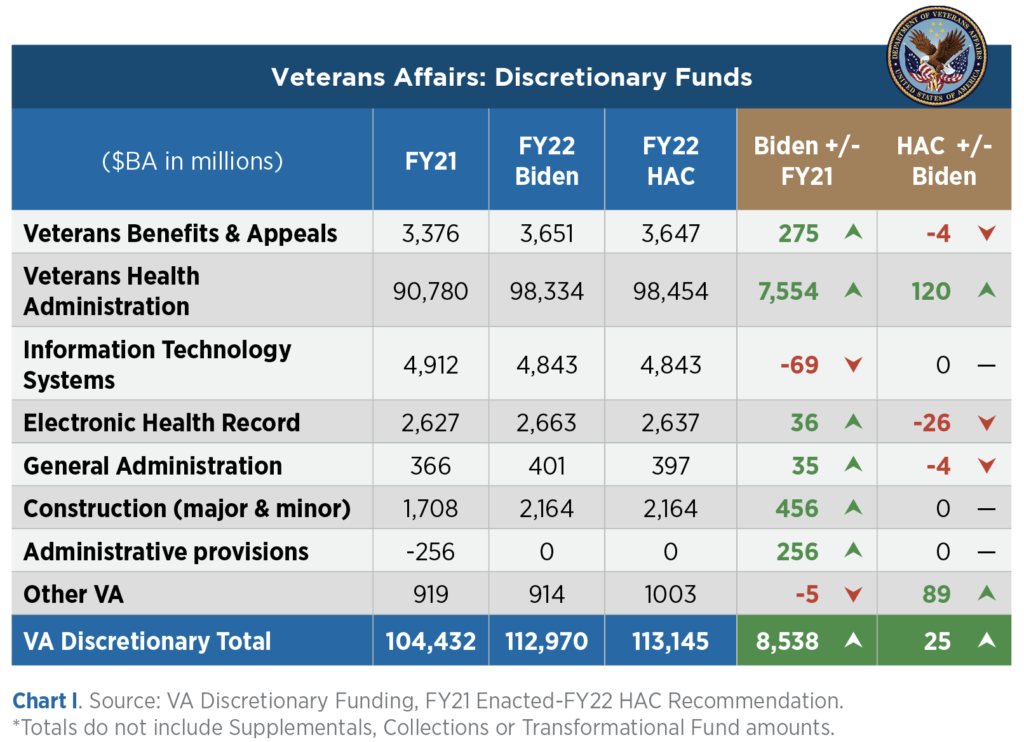

The $113 billion total covers health care, research, information technology, administration and facility maintenance and construction. Veterans Health Administration (VHA), funded at $98.5 billion by HAC, a $7.6 billion or 8% increase, drives most of the VA increase. Within VHA, Community Care, medical services by private providers outside of VA facilities, is the fastest growing element, increasing by 26% from FY21 to FY22 ($18.5B to $23.4B). In contrast, in-house VA medical services increased by 2%.
The House level exceeds the Biden request in Medical Services (+$100M), research (+$20M), grants to states for extended care (+$90M), and several small accounts (+2M). The House bill cuts the Biden budget in Electronic Health Record Modernization (EHRM) (-$26M) and three administrative accounts (-$10M).
Cybersecurity
The Committee-approved bill includes all Biden-requested cybersecurity and information security funding, spread across the VA enterprise. The Committee notes the importance of cybersecurity vigilance and highlights VA’s upcoming update of its Cybersecurity Strategy, with publication by the end of calendar 2021.
HAC states the critical need for VA to be in the forefront of information security, especially with the increase in remote access, and to use end-to-end encrypted communications with zero-trust architecture.
Support for VA’s OIT Budget and Supply Chain
The HAC bill includes the full FY22 request for OIT, $4.8 billion, which is a decrease of $32 million from FY21 and agreed with VA’s split between development, O&M, and staffing. In addition, the Committee concurred with VA’s proposed transfer of $670 million to OIT from the Non-recurring Transformational Fund, giving OIT a total of $5.5 billion for FY22, a 12% increase over FY21.
VA will use the $670 million transfer into its Transformational Fund to fund the Infrastructure Readiness Program ($478M) and the financial management and human resources systems ($192M). O&M also includes $361M for Information Security, $62M to evolve VA Cloud, and $137M for Digital GI bill system modernization.
HAC action supports a total of $491M to accelerate VA’s Supply Chain Management Solution, the Defense Medical Logistics Standard Support (DMLSS), from both OIT and VHA funding sources. DMLSS totals are $107M in OIT and $193M in VHA ($91M already provided in advance funding for FY22, and $102M in FY23 advance funding). VA also has $100M for supply chain from the FY22 supplemental (American Rescue Plan Act), which is available through FY23.
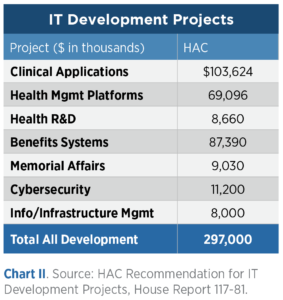
For Development projects, HAC provided detail on the approved projects as seen in Chart II. Within Clinical Applications funding, HAC provides $76M for Supply Chain Management; within Health Management platforms, there is $34M for Community Care and $6.6M for Telehealth development.

Electronic Health Record Modernization (EHRM) Challenges
In response to VA’s “strategic pause” of EHRM, the Committee bill cuts $26M from Biden’s $2.67B FY22 funding plan for EHRM, and withholds 25% of EHRM funding until the Secretary VA provides deployment certifications. The cuts are applied to the contract ($-9M), program management ($-9M), and infrastructure subaccounts ($-8M). HAC-approved $2.64B EHRM funding is available for three years, which is customary for that account. Technical and policy areas of interest for HAC include cybersecurity for EHRM, a blockchain pilot, open architecture, and full use of informatics.
The Committee shares concerns noted in a July 7 Inspector General report that questions ”accuracy and reliability” of EHRM cost estimate data VA provided to the Committee and “directs the Department to swiftly implement the recommended actions and to provide a new estimate.” Subcommittee Chair Wasserman-Schultz (D-FL) stated her intention to hold a EHRM-focused hearing with VA Secretary McDonough. Separately, the House and Senate Veterans Affairs Committees have scheduled July hearings to review IG concerns.
Secretary McDonough announced significant changes to the EHRM program on July 14, including replacing the current parallel deployment plans with an approach that assesses technical and training readiness of each location to determine deployments; creation of a “sandbox,” or a fully simulated testing and training environment; and establishing a unified governance model that includes VA’s clinicians, technical, finance and acquisition experts. The Secretary said deployment schedules will be altered and that Congress had been notified.
Telehealth
The HAC bill fully funds Biden’s $2.6B request for telehealth and connected care, which includes home telehealth, home telehealth prosthetics, and clinic-based telehealth. The Committee directs VA to continue to expand telehealth availability to include additional mental health, primary care, and rehabilitation services, and explore use of telehealth to help with backlogs for disability exams and health care appointments.
HAC also directs VA to seek partnerships to help veterans access telehealth resources, and to adopt telehealth and remote monitoring device systems that are off-the-shelf and device agnostic.
Outlook
The HAC VA spending bill is likely to be included in a multi-bill package (or a “minibus”) that will be considered by the House later this month. IG concerns may trigger EHRM-related amendments and more Congressional hearings, but other IT-related changes are unlikely. FBIQ expects the minibus appropriations package to pass the House before August recess in a partisan vote.